

On the 20th, you make another $30 purchase (balance of $610). On the 12th, you make another $50 purchase (balance of $580). On June 7, you make a $30 purchase, bringing your balance to $530. At the end of the billing cycle, the credit card provider will find the average of your daily balances and use this to determine your finance charges.įor example, imagine you start the billing cycle on June 1 with a $500 credit card balance on a card with an 18% APR. In this method, finance charges are calculated based on your balance at the end of each day.

It’s also referred to as straight average daily balance and true actuarial average daily balance.
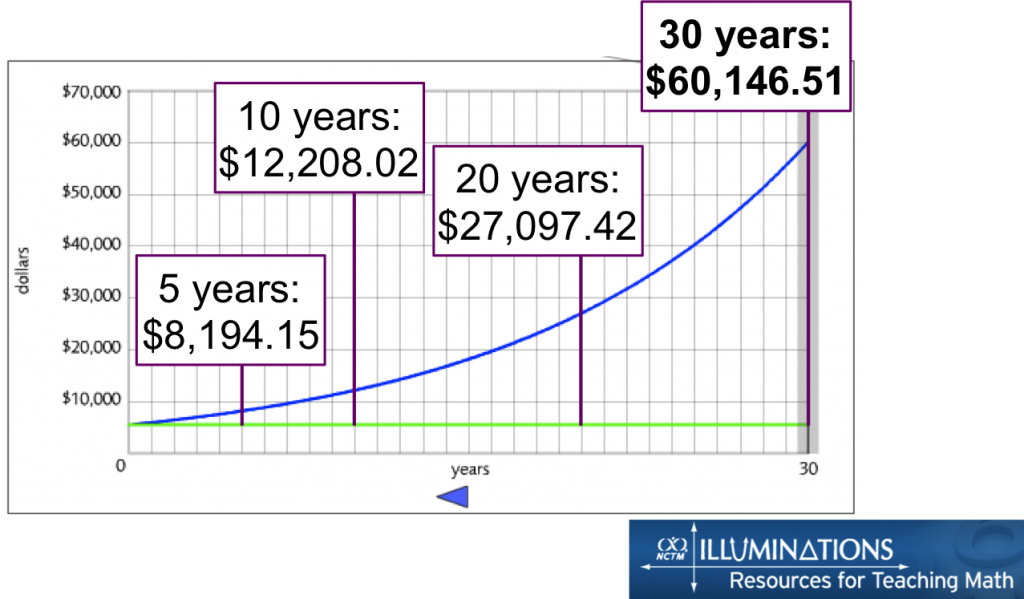
Most credit card finance charges are calculated using a method called the average daily balance. But again, it only refers to the costs for a single year and may not take fees into account.Ĭredit cards provide revolving credit: There is no set date that the balance must be paid off by, and it will keep accruing finance charges until it hits zero. The annual percentage yield (APY) is a bit more accurate as it takes compounding interest into account. Additionally, it doesn’t always include fees, and it only expresses these charges yearly, not for the lifetime of the loan.
#Compound define finance full#
However, a loan’s APR doesn’t give the full picture of the finance charge, as it doesn’t include compound interest costs. The finance charge for a loan is often expressed as the annual percentage rate (APR), which refers to the yearly cost of interest (and sometimes fees) for a loan. But some finance charges can be flat fees that are independent of the loan amount - i.e., a set $10 fee for borrowing money, no matter how much you borrow. Typically, both of these are calculated as a percentage of the loan amount. When taking out a cash advance, borrowers may need to pay a cash advance fee. For example, when taking out a mortgage loan, borrowers may need to pay loan origination fees (the fee to start the loan). However, there are other types of finance charges as well. Interest can either be compounding (interest gets charged on unpaid interest) or non-compounding (interest is only charged on the principal). One of the most common finance charges is interest, a recurring charge that is typically calculated as a percentage of the principal amount (the amount of the loan). Think of finance charges as the cost of the lender’s services. Without finance charges, there would be no reason for a lender to give loans outside of kindness and goodwill. Giving out a loan is risky - There’s no guarantee that the borrower will ever pay it back. These fees incentivize lenders to make loans. Unless you’re borrowing from a friend or family member, taking advantage of an interest-free financing period, or you’ve found an interest-free balance transfer offer without a balance transfer fee, you’ll almost always need to pay some type of fee when you borrow money. When you borrow money from a lender, you rarely get that money for free. It may be charged at the start of a loan, at the end of each billing cycle, when a loan period is extended, or at the end of each day (typically compound interest ). Essentially, it’s the cost of borrowing money. A 40-year-old, on the other hand, would need to save $18,227, or almost three times that amount, to attain the same goal.A finance charge is any cost or fee directly associated with borrowing money. If the objective is to save $1 million by retirement at age 65, based on a CAGR of 6%, a 25-year-old would need to save $6,462 per year to attain this goal.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
